Mysql InnoDB Storage Engine
一、InnoDB Architecture

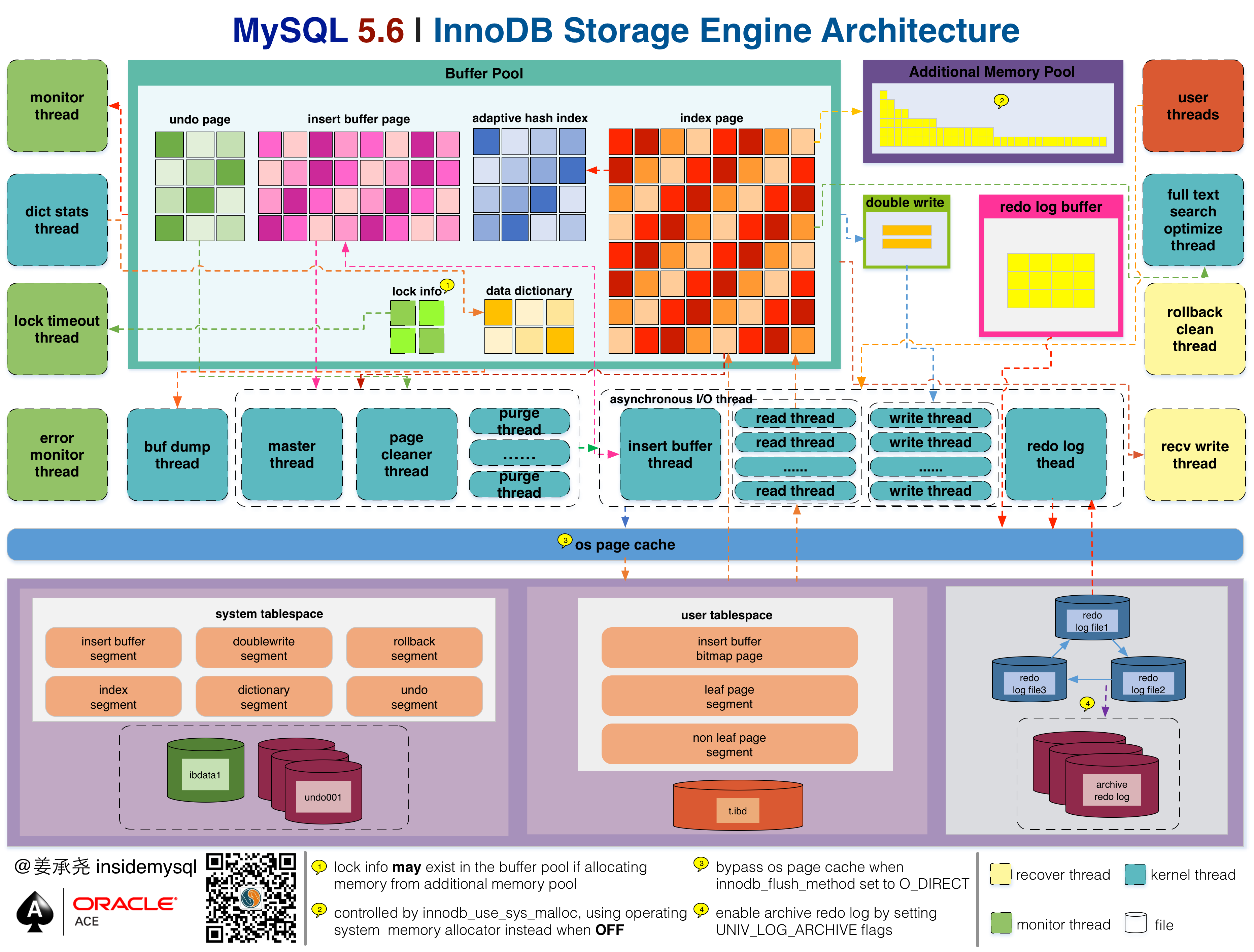
1.1、InnoDB In-Memory Structures
Buffer Pool
Change Buffer
Adaptive Hash Index
Log Buffer
Buffer Pool
缓存table& index,加速读(通常物理机80%以上的内存被分配给buffer pool)
预读
LRU
- 缓冲池污染
Change Buffer
Caches changes to secondary index page,加速写(INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE)
如果每次修改二级索引都直接写入磁盘,会有大量的随机IO
早期支持缓存Insert,叫Insert Buffer
In memory, the change buffer occupies part of the buffer pool
Change Buffer的内部实现也是B+树
Adaptive Hash Index
自适应哈希索引(AHI)查询非常快,一般时间复杂度为 O(1),相比 B+ 树通常要查询 3~4次,效率会有很大提升
Log Buffer
The log buffer is the memory area that holds data to be written to the log files on disk
Redo Log Buffer
Undo Log Buffer
1.2、 InnoDB On-Disk Structures
Tables
Indexes
Tablespaces
Doublewrite Buffer
Redo Log
Undo Logs
二、 InnoDB数据写入流程

三、Mysql InnoDB 数据可靠保证
Log Buffer刷盘 :WAL+CheckPoint
- innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit
Binlog同步
- sync_binlog
Double Write
Redo Log & Binlog 一致性
- 2PC
Crash Safe:Log Buffer、Buffer Pool、Redo Log
四、InnoDB and the ACID Model
A: atomicity.
- undo log
- Two phase Commit
- 2PC→3PC or 1PC(Prepare完成,Commit可以异步)
- 应用层:TCC
C: consistency.
Doublewrite
crash recovery
I:: isolation.
ANSI SQL-92 (RR不解决幻读,InnoDB的RR实现避免了幻读)
Critique:更严谨的隔离级别
- 幻读
- 写倾斜 Write skew
Multi-versioning
InnoDB locking
D: durability.
Doublewrite Buffer
innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit
sync_binlog
innodb_file_per_table
the write buffer in storage device, such as a disk drive, SSD, or RAID array
A battery-back cache in a storage device.
五、Mysql InnoDB Locking
锁类型(lock_type):表锁 VS 行锁 – 描述的是锁的粒度
表锁
表锁(分 S 锁和 X 锁)
意向锁(分 IS 锁和 IX 锁)
LOCK_AUTO_INC:自增锁;
行锁
LOCK_ORDINARY(Next-Key Lock)(分 S 锁和 X 锁)
LOCK_GAP(分 S 锁和 X 锁)
LOCK_REC_NOT_GAP(分 S 锁和 X 锁)
LOCK_INSERT_INTENSION
锁模式(lock_mode):读锁 VS 写锁 – 描述的是加的什么锁
LOCK_IS:读意向锁;
LOCK_IX:写意向锁;
LOCK_S:读锁;
LOCK_X:写锁;
锁思想:乐观 VS 悲观锁
插入意向锁(Insert Intention Locks)
插入意向锁是一种特殊的间隙锁,有些地方简称II GAP,这个锁表示插入的意向,只有在INSERT的时候才会有这个锁。注意,这个锁虽然也叫意向锁,但是和上面介绍的表级意向锁是两个完全不同的概念。插入意向锁和插入意向锁之间互不冲突,所以可以在同一个间隙间隙中有多个事务同时插入不同索引的记录。
譬如在上面的例子中,id = 1 和 id = 5 之间如果有两个事务要同时分别插入 id = 2 和 id = 3 是没问题的,虽然两个事务都会在 id = 1 和 id = 5 之间加上插入意向锁,但是不会冲突。
- 插入意向锁不影响其他事务加其他任何锁。也就是说,一个事务已经获取了插入意向锁,对其他事务是没有任何影响的;
- 插入意向锁与间隙锁和 Next-key 锁冲突。也就是说,一个事务想要获取插入意向锁,如果有其他事务已经加了间隙锁或 Next-key 锁,则会阻塞。
隐式锁
当事务需要加锁的时,如果这个锁不可能发生冲突,InnoDB会跳过加锁环节,这种机制称为隐式锁。隐式锁是InnoDB实现的一种延迟加锁机制,其特点是只有在可能发生冲突时才加锁,从而减少了锁的数量,提高了系统整体性能。另外,隐式锁是针对被修改的B+ Tree记录,因此都是记录类型的锁,不可能是间隙锁或Next-Key类型。
隐式锁中有个重要的元素:事务ID(trx_id)。隐式锁的逻辑过程如下:
A. InnoDB 的每条记录中都有一个隐含的 trx_id 字段,这个字段存在于簇索引的 B+Tree 中;
B. 在操作一条记录前,首先根据记录中的 trx_id 检查该事务是否是活动的事务(未提交或回滚),如果是活动的事务,首先将隐式锁转换为显式锁(就是为该事务添加一个锁);
C. 检查是否有锁冲突,如果有冲突,创建锁,并设置为 waiting 状态;如果没有冲突不加锁,跳到 E;
D. 等待加锁成功,被唤醒,或者超时;
E. 写数据,并将自己的 trx_id 写入 trx_id 字段。隐式锁的特点是只有在可能发生冲突时才加锁,减少了锁的数量。另外,隐式锁是针对被修改的 B+Tree 记录,因此都是 Record 类型的锁,不可能是 Gap 或 Next-Key 类型。
- INSERT 操作只加隐式锁,不需要显示加锁;
- UPDATE、DELETE 在查询时,直接对查询用的 Index 和主键使用显示锁,其他索引上使用隐式锁。
理论上说,可以对主键使用隐式锁的。提前使用显示锁应该是为了减少死锁的可能性。INSERT,UPDATE,DELETE 对 B+Tree 们的操作都是从主键的 B+Tree 开始,因此对主键加锁可以有效的阻止死锁。
六、InnoDB Multi-Versioning
事务版本号
表的隐藏列。
undo log
read view
Multi-Versioning and Secondary Indexes
灵魂拷问:覆盖索引,MVCC是否需要回表?
详见:MySQL :: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 15.3 InnoDB Multi-Versioning
七、InnoDB and Mysql Replication
7.1、MySQL Asynchronous Replication
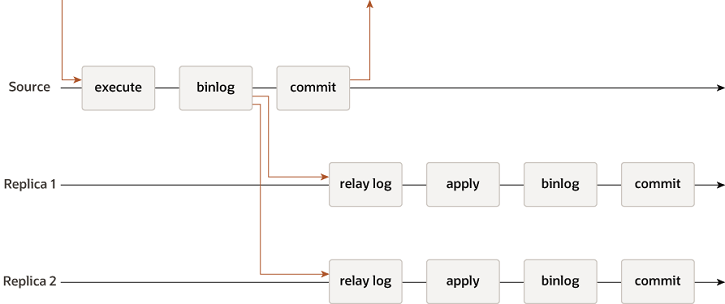
7.2、MySQL Semisynchronous Replication
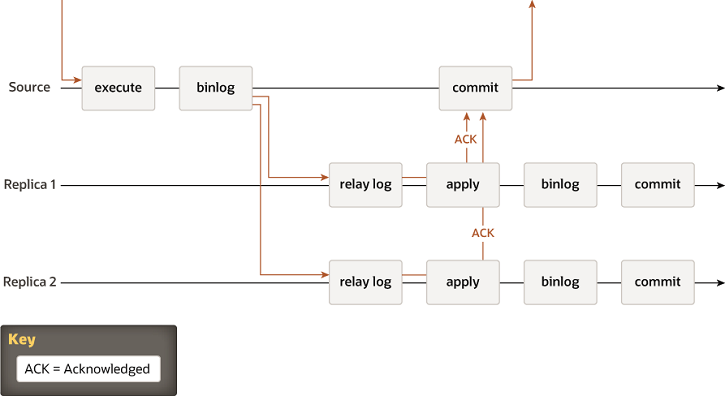
AFTER_COMMIT
rpl_semi_sync_master_wait_point
AFTER_COMMIT(5.6默认值)
AFTER_SYNC(5.7默认值,但5.6中无此模式)

半同步复制降级
- rpl_semi_sync_master_timeout
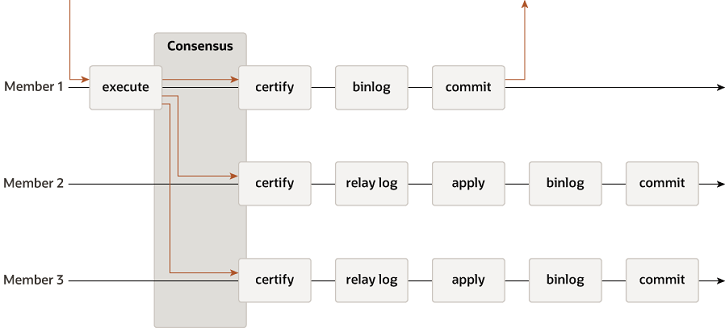
7.3、MySQL Group Replication Protocol
并行复制
- 基于GTID,主库上Group Commit,从库依然可以commit
Mysql Group Replication缺点
大事务卡顿
有限制,每张表要有主键,用于write set冲突检测
八、Mysql 高可用
问题:mysql主节点宕机了,会怎样,如果要实现高可用可以怎么做,有哪些常见方案
Master-Slave模型
故障检测
故障转移
脑裂问题
数据一致性
半同步复制
异步复制
同步复制
MHA: 仅负责MYSQL的高可用, 三次连接主库失败, 会认为主库失败. 执行切主. 问题: manager 单点 无人维护. 架构图. MGR: MySQL 5.7.17版本中以插件形式推出的方案, 通过对事物的hook实现的, 将事物的信息(binlog、gtid) 封装成 paxos 协议发送到其他节点内. 其他节点检查通过后进行提交 (冲突检测). 支持自动故障转移 通过paxos协议实现. 支持单主和多主(冲突的可能大, 不建议) 必须需要打开gtid. 基于paxos, 写入延迟大 Orchestrator: 自动故障转义、手动主从切换、复制拓扑调整. 界面丰富 通过raft 解决自身的高可用. Orchestrator 节点集群中一个leader, hook 的抽象和处理. 如何判断master宕机: 本身连不上主,可以连上该主的从,则通过从去检测,若在从上也看不到主(IO Thread),则判断Master宕机 开源的 Orchestrator 也是基于 vip的
双机房同步
参考Otter等解决方案
数据回环
数据冲突解决
- 避免冲突, 单元化
- lww: last write win,
- Trusted Source: 指定机房为准,
- 冲突暴露给业务方
- 自定义冲突解决方案
拓扑解决
九、FAQ
为什么有Redo log还要有binlog,两者的区别是什么,有没有可能合并成一个log
Redo log: InnoDB层面,物理逻辑日志,Binlog Mysql层面物理日志,用于实现主从复制
可以合并,合并后优势也不明显
Mysql怎么做保证可靠
Mysql事务隔离级别,默认是什么级别,怎么实现的?
幻读是什么,跟可重复读的区别是什么,Mysql RR 隔离级别到底能否避免幻读?
幻读强调row sets,多行,Mysql SQL 92标准 RR隔离级别不能避免幻读,但是Mysql InnoDB未严格按照SQL 92标准,通过next-key lock避免了幻读:
快照读,通过MVCC避免幻读
当前读,通过next-key lock避免幻读
Mysql 如何实现MVCC,Read View怎么确定,RR、RC有什么区别?
Mysql主从切换如何做到不丢数据
Mysql并行复制的底层逻辑是什么?
Mysql有哪些常见的高可用方案,怎么选型?
Mysql InnoDB什么时候需要分表
分表影响什么:B+树的树高
分表的依据:压测
参考文档
MySQL :: MySQL 8.0 Reference Manual :: 15 The InnoDB Storage Engine

