Fault tolerance and high avaliability
前言
- Availability
- Service-Level Objective(SLO)
- e.g. 99.9% of requests in a day get response in 200 ms
- Service-Livel Agreement(SLA)
- Service-Level Objective(SLO)
- Achieving high availability : fault tolerance
- Failure: system as a whole isn’t working
- Fault: some part of system isn’t working
- Node fault
- Network fault
- Fault tolerance
Trade-off: performance and consistency
牺牲window的consistency来换取性能?
“少数服从多数”的方式也有一些劣势,为了保证 leader 选举的正常进行,它所能容忍的失败的 follower 数比较少,如果要容忍 1 个 follower 挂掉,那么至少要 3 个以上的副本,如果要容忍 2 个 follower 挂掉,必须要有 5 个以上的副本。也就是说,在生产环境下为了保证较高的容错率,必须要有大量的副本,而大量的副本又会在大数据量下导致性能的急剧下降。这种算法更多用在 Zookeeper 这种共享集群配置的系统中而很少在需要大量数据的系统中使用的原因
理论基础
- RSM
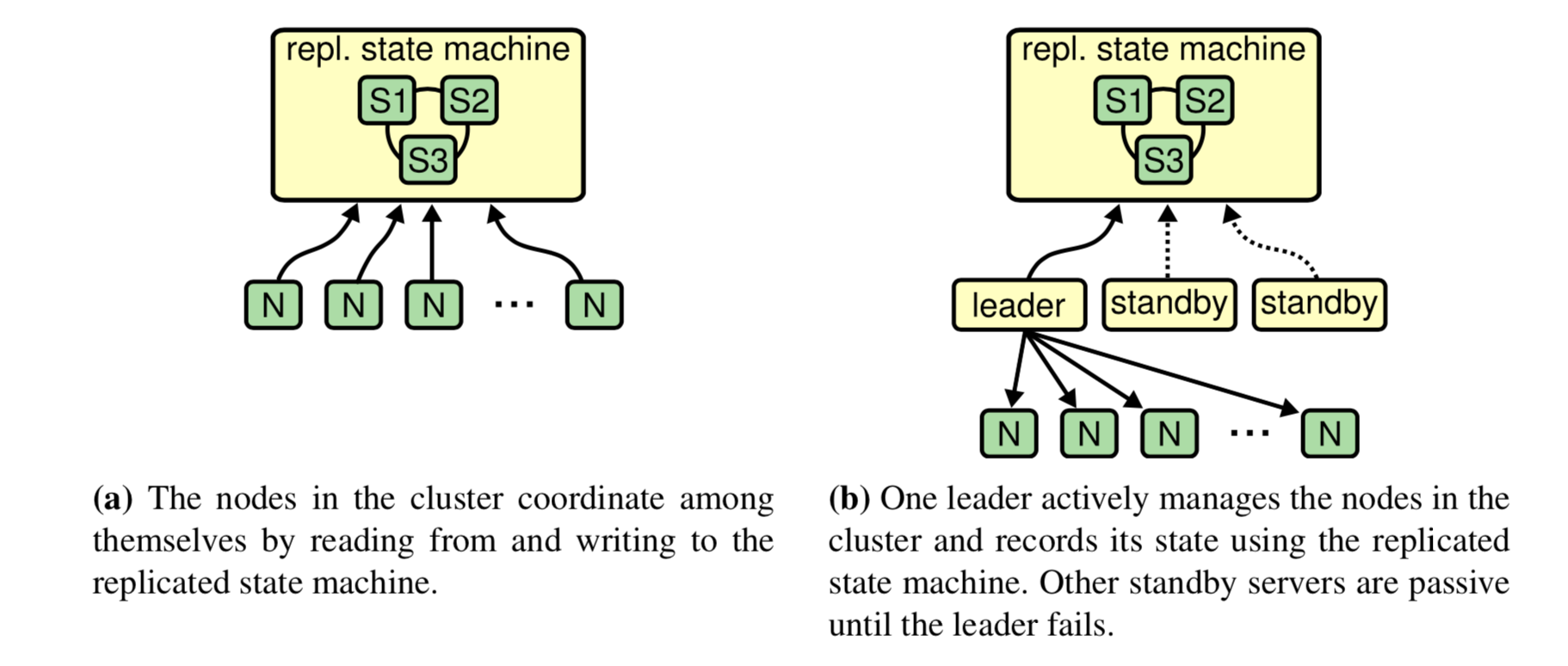
Tolerance
Fualt detection
- Typical implementation
- send message,await response,lable node as crashed if no reply within some timeout
- Problem
- cannot tell the difference between crash node, temporarity unresponsive node,lost message, and delayed message
- Failure detection in partially synchronous systems
- Typical implementation
Leader Election
- 怎么选取新的leader?
- 怎么保证或尽可能保证数据一致性?
- Follower log repair
split-brain
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Split-brain_(computing)
Approaches for dealing with split-brain
classify them as either optimistic or pessimistic.
- Quorum-consensus
- Fencing
Log Replication
- Quorums
- Two common approaches
- Last writer wins(LWW) e.g. lamport clock
- Multi-value register e.g. vector clock
- any/one
- ISR(In-Sync Replicas)
Log Compaction
工程投影
Mysql HA
Mysql高可用架构:MM keepalived → MHA→Orchestrator→MGR/Galera
Mysql MHA
MHA performs automating master failover and slave promotion with minimal downtime, usually within 10-30 seconds. MHA prevents replication consistency problems and saves on expenses of having to acquire additional servers. All this with zero performance degradation, no complexity (easy-to-install) and requiring no change to existing deployments.
Failure Detection
MHA Manager checks only single route: From Manager to Master. (By default,But this is not recommended. )
two or more checking routes by calling an external script defined at secondary_check_script parameter
Leader Election
candidate_master>lastest slave>section name in config file order
If hosts meet the above criteria, new master is determined based on the following rules.
- If you set candidate_master=1 on some hosts, they will be prioritised.
- If some of them are the latest (slaves that have received the latest binary log events), the host will be selected as a new master
- If multiple hosts are the latest, a master host will be determined by “order by section name in the config file”. If you have server1, server2, and server3 sections and both server1 and server3 are candidate_master and the latest, server1 will be selected as a new master.
- If none of servers set candidate_master=1, the latest slave server will be the new master. If multiple slaves are the latest, order by section name rule will be applied.
- If none of the latest slaves can be new master, one of the non-latest slaves will be new master. Order by section name rule will also be applied here.
- If you set latest_priority parameter to 0, “whether the slave is the latest or not” does not matter to decide new master at all. If you want to fully control priorities for the new master (you can decide rules in the config file: order by section name), using this parameter may help.
Brain-Split
- optionally 7-10 seconds to power off the master machine to avoid split brain
- Custom Extension:shutdown scprit: For forcing shutdown the master
- shutdwon process
- power off the machine
If shutdown script exit code is other than 0 or 10(failed), MHA Manager aborts failover.
Consistency
(almost) no data loss,By using together with Semi-Synchronous Replication
- Semi-Synchronous
- prevents replication consistency problems
- Online switching master to a different host:blocking writes
- automating master failover:Saving binary log events from the crashed master (if possible)
- If the dead master is reachable via SSH, copying binary logs from the latest slave’s end_log_pos (Read_Master_Log_Pos)
RTO(Recovery Time Objective)
- 故障切换:10~30 seconds(有些场景无法切换)
- Failure detection: 9~12s
- secondary_check_script: For checking master availability from multiple network routes
- avoid split brain: (optional)7~10s
- apply differential relay logs to new master:a few seconds
- Failure detection: 9~12s
- 正常切换:within mere seconds (0.5-2 seconds) of downtime (blocking writes only)
存在的问题
- MHA manager 单点
- 有些场景无法自动切换,强制切换可能会面临数据一致性问题
- brain-split,虽然MHA shutdown-script可一定程度避免脑裂,但shutdown操作风险较大,e.g. shutdown new master切换失败;
Orchestrator
Orchestrator跟MHA本质上类似,相当于改良版的MHA(一定程度上也引入了复杂性),最核心的点在于引入Raft协议:
orchestrator/raftdeployments solve both high-availability fororchestratoritself- as well as solve issues with network isolation, and in particular cross-data-center network partitioning/fencing.详见:orchestractor/raft:fencing
存在的问题
Raft consensus协议主要是解决orchestrator的HA问题,对于Orchestrator管理的数据库Leader Election并不是通过Raft实现,所以一下问题依然存在:
- 有些场景无法故障转移,强制切换可能会面临数据一致性问题;
- 解决脑裂问题仍然有一定挑战,解决了network isolation场景下的脑裂,但是无法彻底避免脑裂;
具体实践见:GitHub 的高可用性方案:orchestrator、Consul 和 GLB
Mysql Group Relication
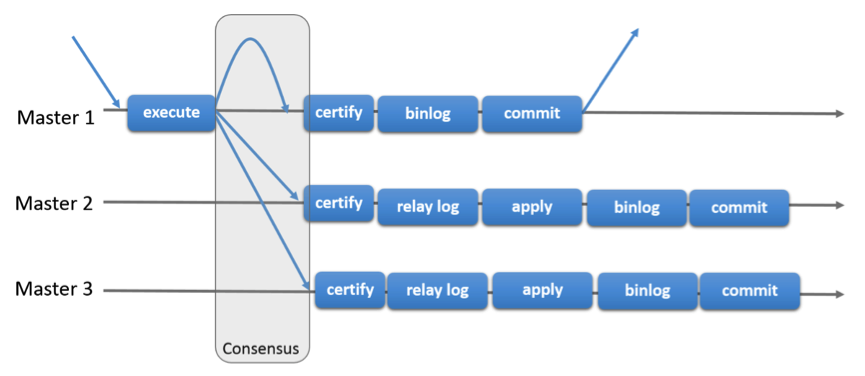
不同节点间没有分布式锁,所以无法使用封锁来避免。为提高性能,Group Replication乐观地来对待不同事务间的冲突,乐观的认为多数事务在执行时是没有并发冲突的
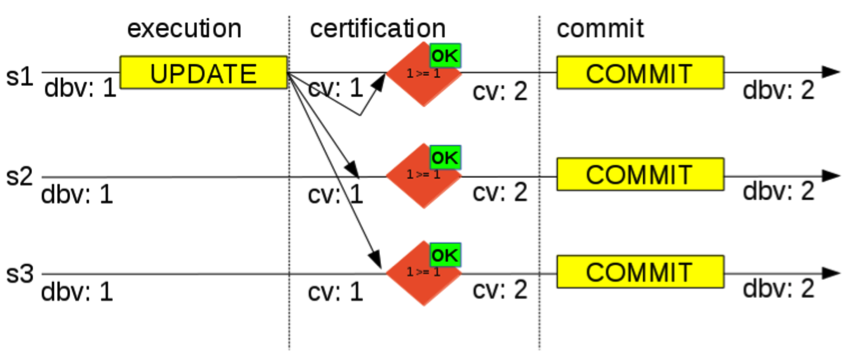
####
一些限制
- Group Replication中每个表必须定义一个主键,副组织需要利用唯一健来作为每一行数据的唯一标识,从而是的组能够准确的确定每个事务修改了哪些行,一遍能够判断哪些事务存在冲突
- 事务大小限制:如果事务产生的消息内容过大,以至于通过网络无法在5s内在组成员之间复制消息,可能会判定成员失败;
存在的问题:
网络环境差和大事务场景下表现不好:
- 依赖paxos xcom实现consensus,原子广播的突出优点是在低延迟局域网有很高的吞吐率。反之multi-primary mode在跨机房不稳定的网络环境表现不好
The MySQL Group Replication documentation isn’t very optimistic on WAN support, claiming that both “Low latency, high bandwidth network connections are a requirement” and “Group Replication is designed to be deployed in a cluster environment where server instances are very close to each other, and is impacted by both network latency as well as network bandwidth.”
- MGR事务认证需要write_set,大事务涉及的write_set过大也会影响性能,容易hung住;
Redis cluster
High performance and linear scalability up to 1000 nodes
consistency guarantees
Redis不保证强一致性,主要是基于性能和一致性的取舍;
Redis支持synchronous writes,在sychronous的模型下,仍然不支持强一致性;
Redis Cluster is not able to guarantee strong consistency.
Basically, there is a trade-off to be made between performance and consistency.
Redis Cluster has support for synchronous writes when absolutely needed, implemented via the WAIT command. This makes losing writes a lot less likely. However, note that Redis Cluster does not implement strong consistency even when synchronous replication is used: it is always possible, under more complex failure scenarios, that a replica that was not able to receive the write will be elected as master.
Failure Detection
在一个NodeTimeout时间之后还未收到新的ping消息,就会标记PFail,当集群中的大多数节点都标记PFail,就会判定未Fail
heartbeart:Ping/pong
gossip
PFAIL:prossible failure
FAIL:Node is failing, confirmed by a majority of masters within a fixed amount of time.
Leader Election
- epoch:logical clock
- configEpoch
- repl_offset:offset越大,随机休眠的时间越短,越有机会被选举
- majority
Brain-split
PFAIL -> FAIL 的转变使用一种弱协议(agreement
- gossip
- epoch
消息队列
Kafka
Kafka中Fault Detection、Leader Election依赖zk
数据可靠性
高可靠配置:
topic 的配置:replication.factor>=3, 即副本数至少是 3 个;2<=min.insync.replicas<=replication.factor
broker 的配置:leader 的选举条件 unclean.leader.election.enable=false(只有在ISR中才可以参与选举)
producer 的配置:request.required.acks=-1(all),producer.type=sync(ISR中的所有节点收到才发送下一条)
| **ISR | HW | ACK:** |
当request.required.acks=1(默认)时,如果Leader A宕机,Follow B被选举为新的leader,那么“6”会被丢失;
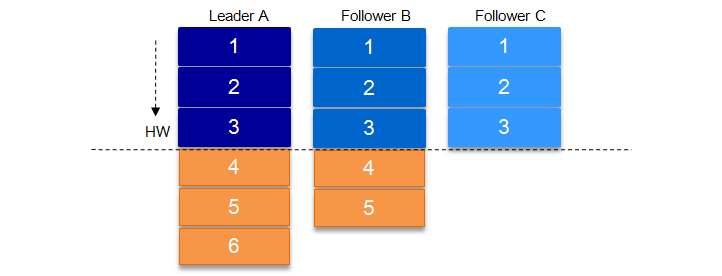
如上图,某个 topic 的某 partition 有三个副本,分别为 A、B、C。A 作为 leader 肯定是 LEO 最高,B 紧随其后,C 机器由于配置比较低,网络比较差,故而同步最慢。这个时候 A 机器宕机,这时候如果 B 成为 leader,假如没有 HW,在 A 重新恢复之后会做同步 (makeFollower) 操作,在宕机时 log 文件之后直接做追加操作,而假如 B 的 LEO 已经达到了 A 的 LEO,会产生数据不一致的情况,所以使用 HW 来避免这种情况。A 在做同步操作的时候,先将 log 文件截断到之前自己的 HW 的位置,即 3,之后再从 B 中拉取消息进行同步。
pulsar
Topic Owner → Ledger Client (只有一个ledger Client可写入),Ledger切换通能过fencing机制避免脑裂
fencing
详见:BK Fencing
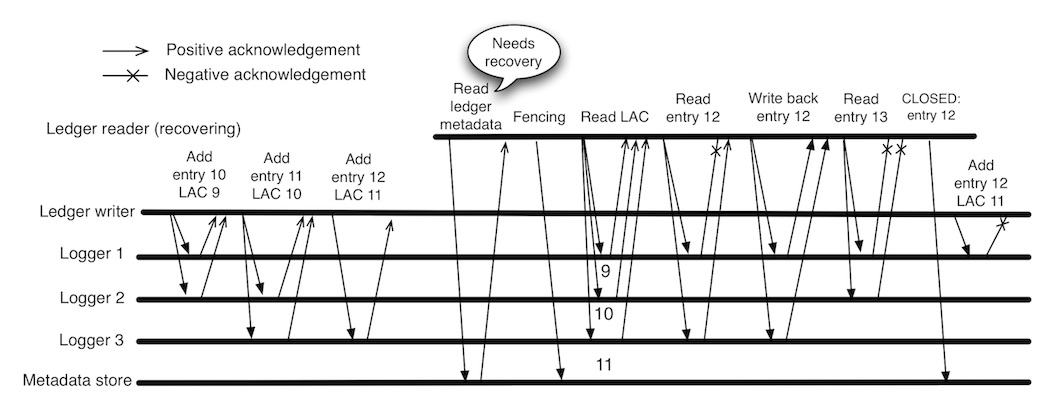
探讨
思考:依赖ZK实现Leader Election,怎么避免脑裂?
e.g.: Kafka broker 怎么避免脑裂?
- Controller进行Full GC停顿时间太长超过zookeeper session timeout 出现假死
- Controller 所在broker网络出现故障
解决方案:
broker leader会维护epoch,选举新的leader epoch会递增,并同步其他的follower,follower会接受epoch更新的leader的请求;
Kafka的Controller也采用了epoch,具体机制如下:
- 所有Broker监控”/controller”,节点被删除则开启新一轮选举,节点变化则获取新的epoch
- Controller会注册SessionExpiredListener,一旦因为网络问题导致Session失效,则自动丧失Controller身份,重新参与选举
- 收到Controller的请求,如果其epoch小于现在已知的controller_epoch,则直接拒绝
理论上来说,如果Controller的SessionExpired处理成功,则可以避免双leader,但假设SessionExpire处理意外失效的情况:旧Controller假死,新的Controller创建。旧Controller复活,SessionExpired处理意外失效,仍然认为自己是leader。 这时虽然有两个leader,但没有关系,leader只会发信息给存活的broker(仍然与Zookeeper在Session内的),而这些存活的broker则肯定能感知到新leader的存在,旧leader的请求会被拒绝
【注】在一个特定的window仍然可能会有脑裂的可能,要完全避免脑裂要么请求每次从zk里面获取最新的leader信息,要么broker自身实现共识协议;
- ZK & HDFS怎么避免脑裂的呢?
小结:当我们谈高可用的时候我们再谈什么
故障恢复时间(RPO)
- 故障探测
- Timeout
- More: select or write
- harnesses the replication topology
- Timeout
- avoid brain-split
- 故障探测
Performance
数据一致性(RTO)
- Leader Election:
- consensus协议:保证新的leader有committed的数据
- promote a candidate master
- Lastest slave
- Leader Election:
brain-split
- Quorum-consensus
- Fencing
其他
- 机器成本
- 运维成本